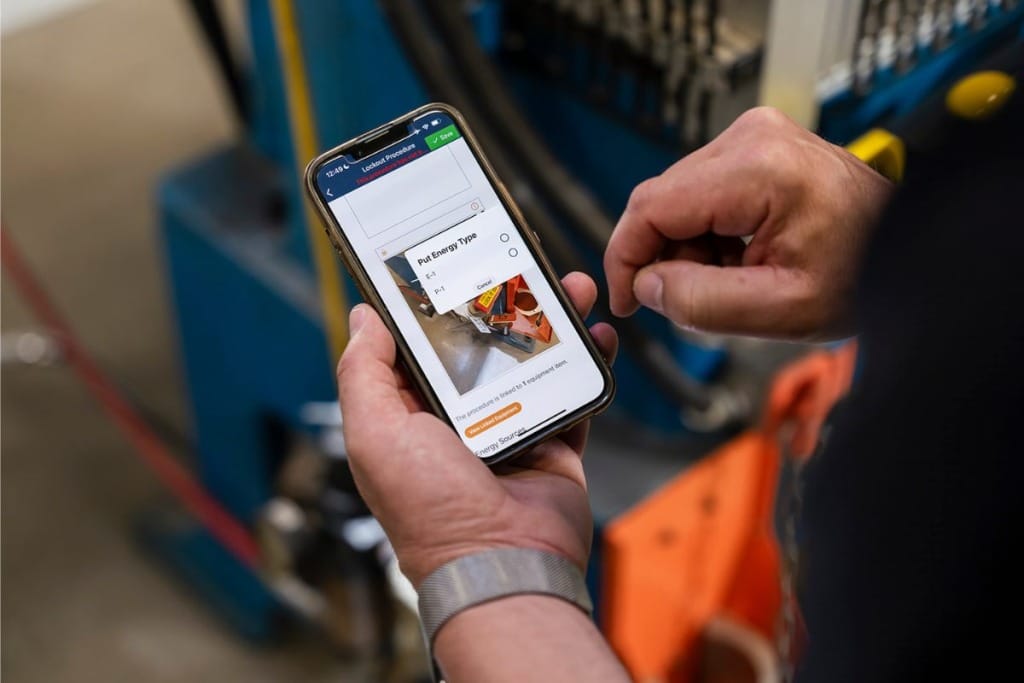
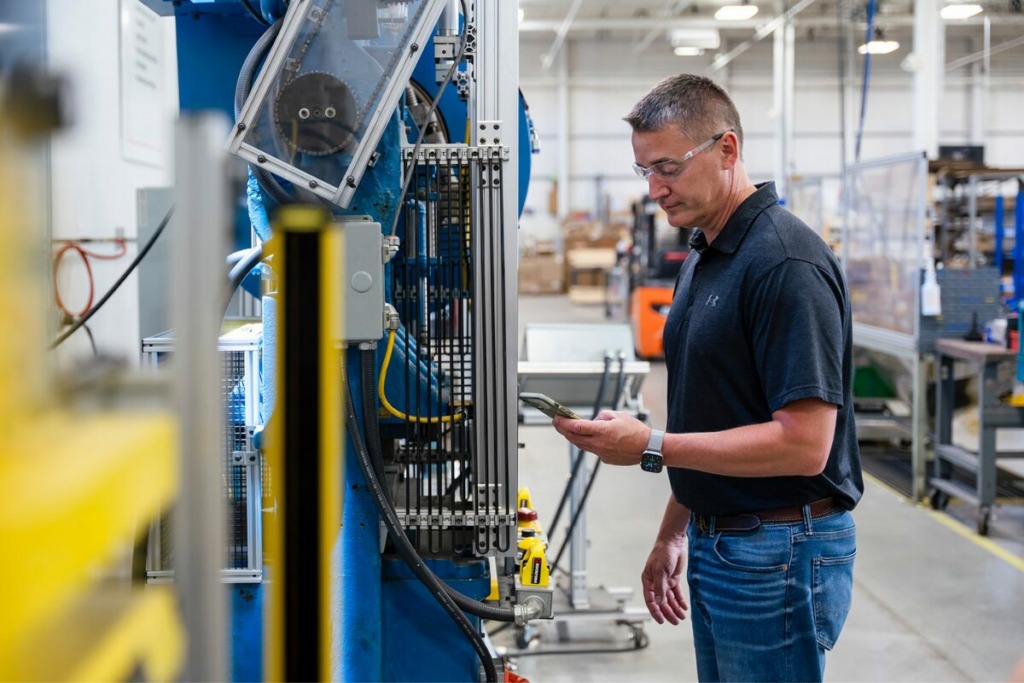
This article is a beginner’s guide to lockout tagout. It dives into what it is, why it’s important, how it is performed, and other key details!!
Providing a safe work environment should be a top priority for any organization, but especially in industries where employees work with machinery, dangerous equipment, and hazardous energy. One of the most effective ways to promote safety and protect workers in these environments is to implement the safety practice lockout tagout (LOTO).
But what exactly is lockout tagout, and why is it so important? In this article, we will discuss the meaning of LOTO, how it works, why it’s essential, and the regulations that guide its implementation.

What is Lockout Tagout?
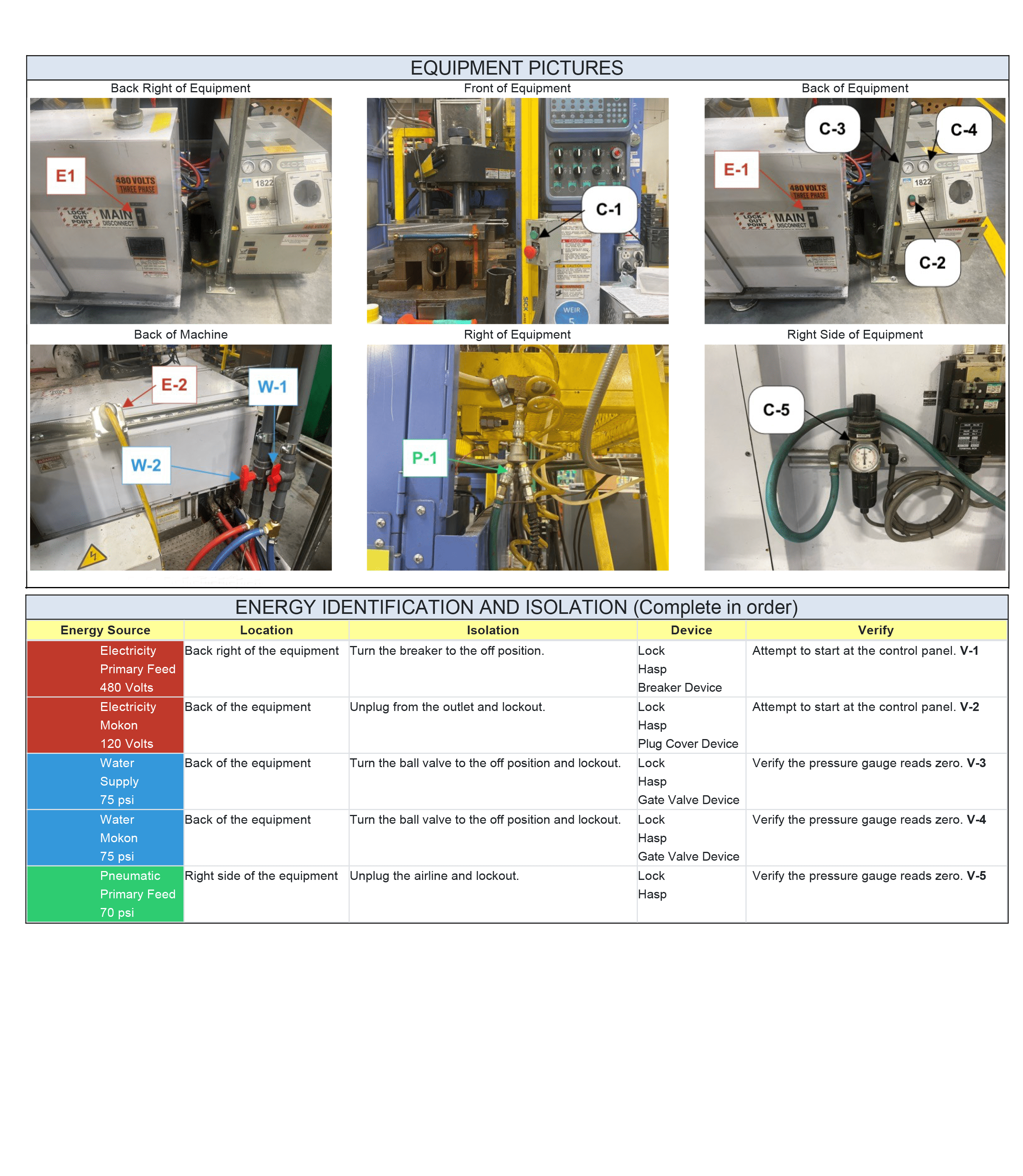
Lockout tagout (LOTO) is a safety practice used to ensure that machines and equipment are properly shut down during maintenance or servicing work. Its purpose is to protect workers from serious injuries or fatalities by preventing accidental startup or energization of equipment. It involves physically locking power sources and placing warning tags on the machine to alert nearby workers that the equipment is off-limits until the procedure is completed and the equipment is returned to service.
So, when should LOTO be performed? What industries need it? Lockout/Tagout should be used any time there is the possibility of unexpected energization, start up, or release of hazardous energy of machines or equipment that could cause injury and harm to workers. This could apply to workers performing repairs, set up, servicing, inspections, cleaning, and other activities.
Because of its role in safety, lockout tagout procedures are often implemented in industries that deal with any form of hazardous energy (such as electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal, and other energy sources).
Steps For Performing Lockout Tagout
Lockout tagout involves a series of steps that work together to allow machinery to be safely shut down, worked on, and then returned to normal service. Here is a quick overview of the 10 steps of lockout tagout.
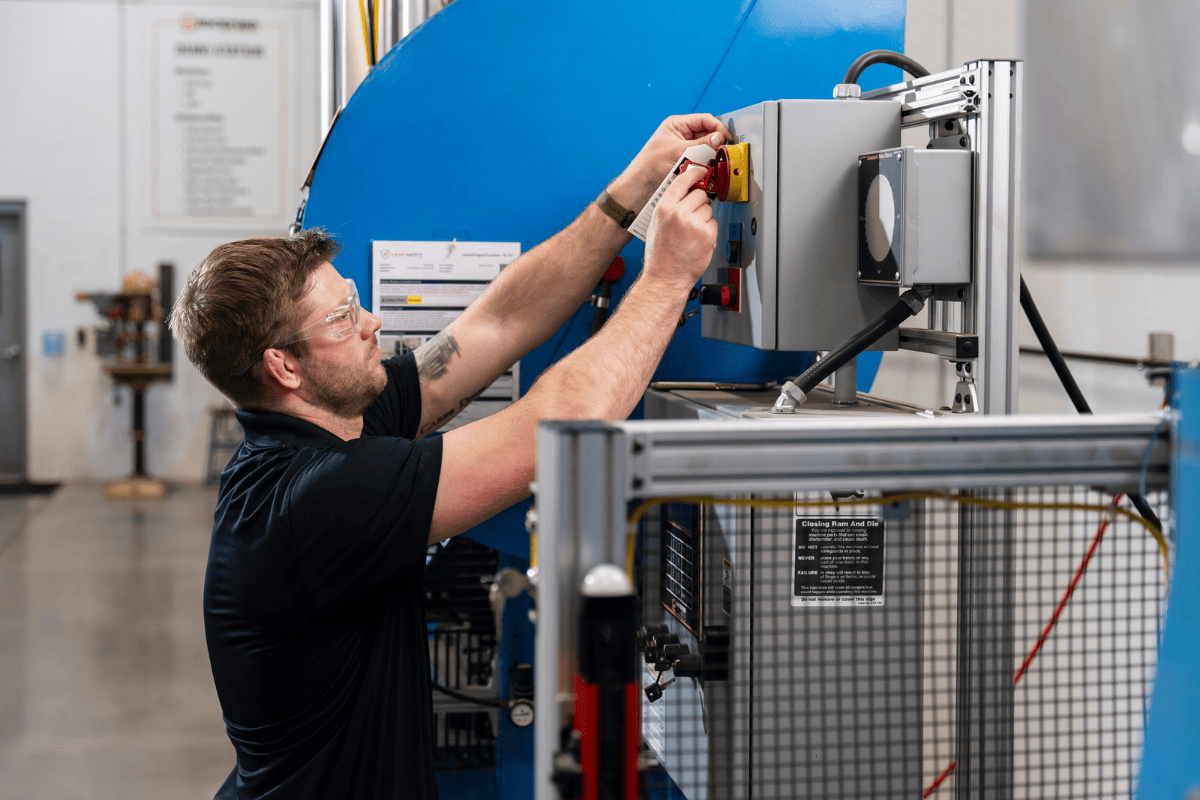

Why is Lockout Tagout Important?
According to OSHA, lockout tagout is estimated to help prevent 120 fatalities and 50,000 injuries every year. This stat highlights how LOTO serves as a critical form of accident prevention in the workplace. Lockout tagout may seem like a non-consequential item on your checklist, but the numbers show that it is a lot more than that.
While lockout tagout is primarily meant to prevent worker injuries, it can also help avoid other profound problems including:
- Equipment Damage – Accidental equipment startups can result in broken machinery or operational failures.
- Compliance Violations – Failure to correctly follow lockout tagout procedures can lead to heavy OSHA fines and penalties.
- Workplace Productivity Loss – Injuries and equipment damage result in downtime, costly repairs, and legal issues.
As per OSHA reports, failure to control hazardous energy is consistently one of the top causes of workplace injuries and deaths, making LOTO an essential safety practice.
Safety Standards Governing LOTO
There are 2 main safety standards that govern lockout tagout in the US: OSHA 1910.147 and ANSI Z244.1. In this section we will briefly go over the main points of each standard. However, you can access a more in-depth guide for each of the standards by clicking the links above.
Companies that comply with both OSHA and ANSI guidelines ensure a higher level of workplace safety and avoid costly violations.
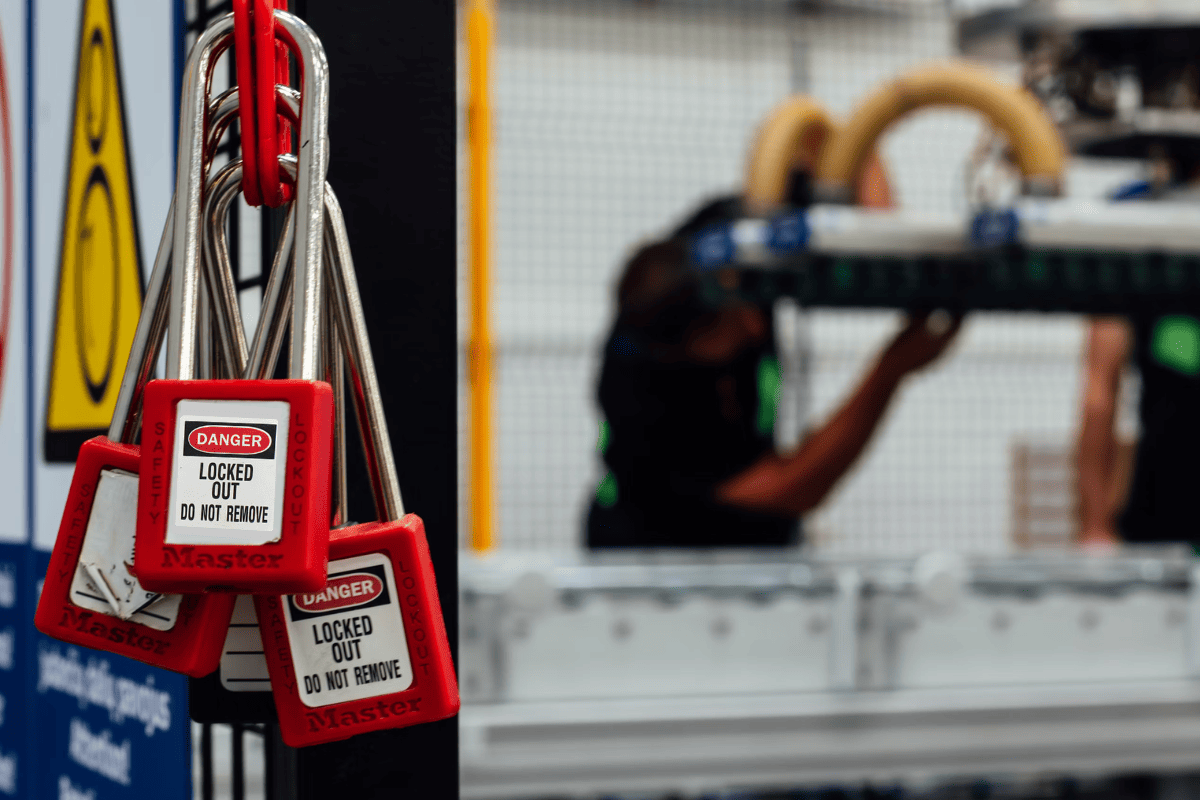

Common Misconceptions
Despite its importance, there are many misconceptions surrounding lockout tagout. In this section we will look at some of the most common misunderstandings about LOTO and set the record straight.
- Misconception: “Lockout Tagout only applies to electrical energy.”
- Truth: LOTO applies to all hazardous energy sources including hydraulic, pneumatic, thermal, and mechanical.
- Misconception: “LOTO is only required for large machines.”
- Truth: Even small equipment can store dangerous energy and must be locked out properly before having any maintenance or servicing activities performed on it.
- Misconception: “Using just a tag is enough.”
- Truth: A lock must always be used in tandem with a tag. The only exception is if the equipment cannot be locked out.
When performing lockout tagout, make sure you are relying on correct information and learning from credible sources. It never hurts to consult a safety standard, experienced coworker, the internet, or trusted articles such as this one to double check.
Conclusion
Lockout Tagout is a critical safety measure that protects workers from hazardous energy during servicing or maintenance on equipment. By following lockout tagout steps, making safety a priority, and complying with OSHA 1910.147/ANSI Z244.1, companies can prevent workplace accidents, protect lives, and maintain compliance.
Note: If your workplace still relies on outdated or inconsistent LOTO procedures, it’s time to improve your program and enhance worker safety. Invest in software to improve your compliance tracking, data history, scheduling, team collaboration, and more!