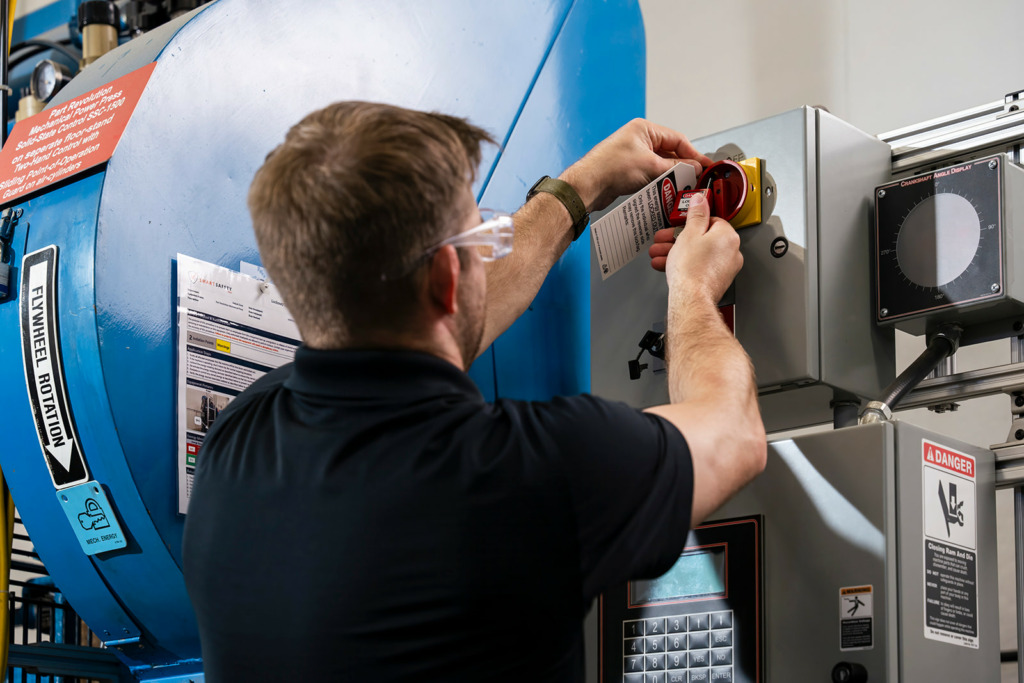
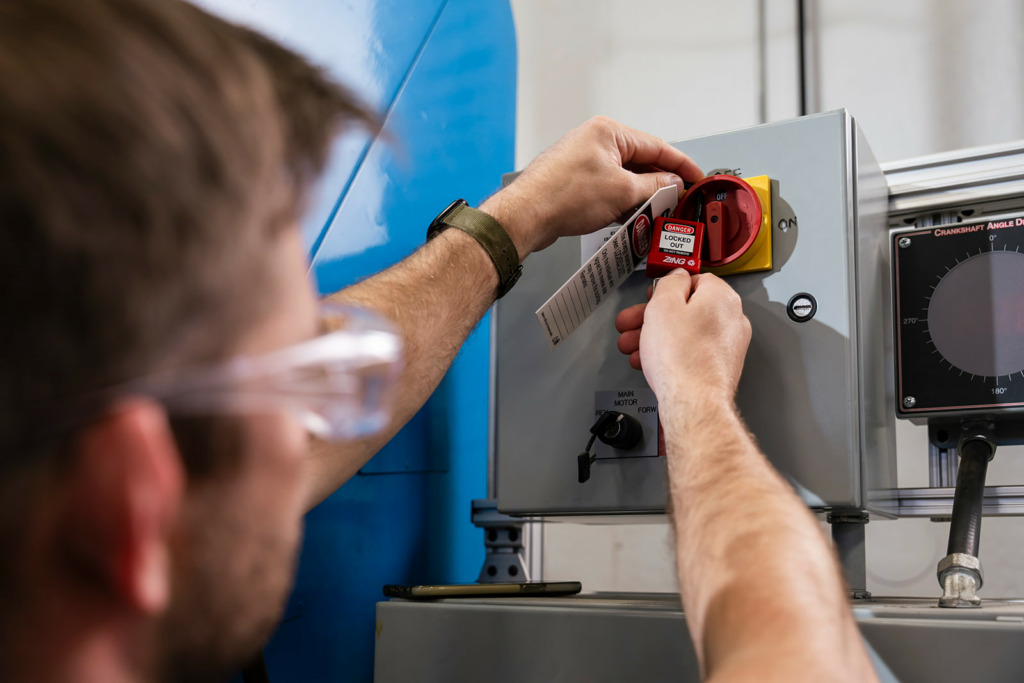
Not sure where to get started with creating a lockout tagout training program? Don’t worry. This article provides all the tips and tricks you need to build an effective LOTO training course.
Are you a building or facility manager? Possibly a supervisor over a workplace safety team? If so, listen up. This article is meant for you.
Lockout tagout is repeatedly reported as one of the top 10 most frequently cited OSHA violations. In fact, it came in at number 3 in 2024, with nearly 3,000 violations. While only some of these violations resulted in a serious injury or death, all of them resulted in hefty fines from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, which I think we all want to avoid.
One of the easiest and most reliable ways to avoid receiving one of these OSHA violations is to provide comprehensive, thorough training to employees. I am here to help you do just that. In this article we will cover key elements of an effective LOTO training program and essential topics to cover. Additionally, I will offer practical tips and resources to enhance employee understanding, retention, and compliance. My goal is to provide you with a foundation, so you can create a lockout tagout training program that is intuitive, informative, and effective. Now, let’s get to it.
Why Lockout Tagout Training Matters
Lockout tagout training is a preventative measure that can lower the risks of injury or accident occurring in your workplace. Of course, it is not a full proof approach. Workers will still make mistakes. After all, I’m sure that some of the companies who received OSHA violations last year had in fact offered training to their employees. However, workers who have been sufficiently educated on lockout tagout are far less likely to engage in risky behavior or improperly perform procedures.
If 2024’s violation stats weren’t enough to persuade you of the importance of lockout tagout training, maybe this will: The OSHA Lockout Tagout Standard (29 CFR 1910.147) legally requires employers to provide their employees with proper training on LOTO procedures.
Hence, providing lockout tagout training not only reduces the likelihood of accidents, but it also supports legal compliance and reinforces a culture of accountability and safety.

What to Train Employees On
When creating a lockout tagout training program, it is important to go back to the basics. As an experienced professional, you may be ready to jump into the latest lockout tagout devices or the intricacies of the machinery; however, you need to start training at the most beginner level. Here are some key topics to train on.
How Often Should Lockout Tagout Training Be Provided?
Once you have a lockout tagout training program set up, you need to actually administer it. Here is some guidance for setting a training schedule.
- Initial Training: Make sure that all new hires receive an initial training. This will help them adjust to the new work setting, understand their role, and better integrate into the team. If you have any company-specific procedures or rules, now is the time to go over them.
- Annual Refresher: As a rule of thumb, provide a refresher training course every 12 months to ensure that employees are updated on current procedures and understand how to perform their duties properly.
- Policy/Procedure Updates: As needed, provide training on topics such as new equipment, revised procedures, changed regulations, and new company operations.
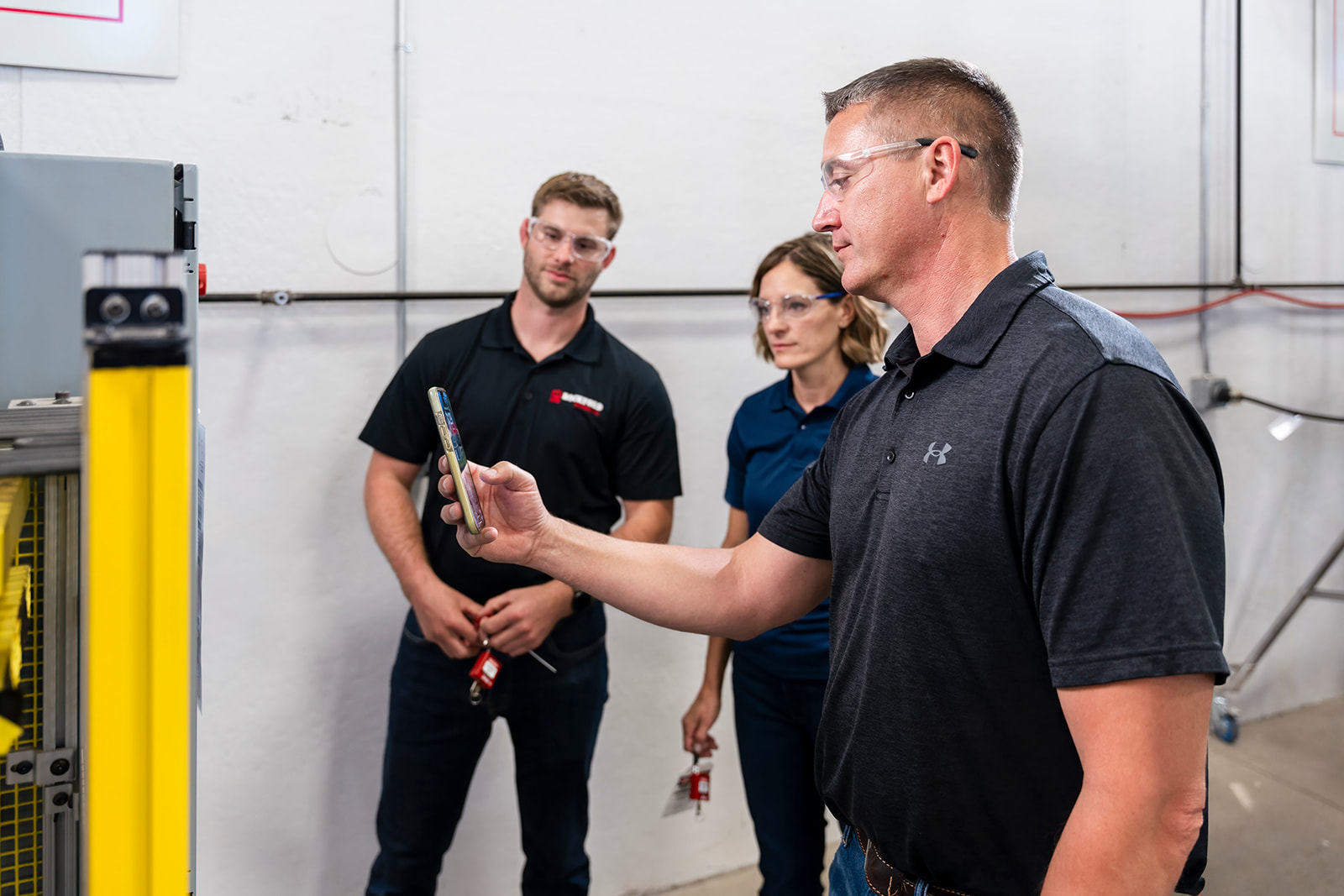

Tips for More Effective Lockout Tagout Training
1. Use Real Equipment for Demonstration – LOTO is very hands-on, and lockout tagout training should be as well. Let trainees try handling the equipment, physically isolating energy sources, and applying locks/tags in a controlled setting.
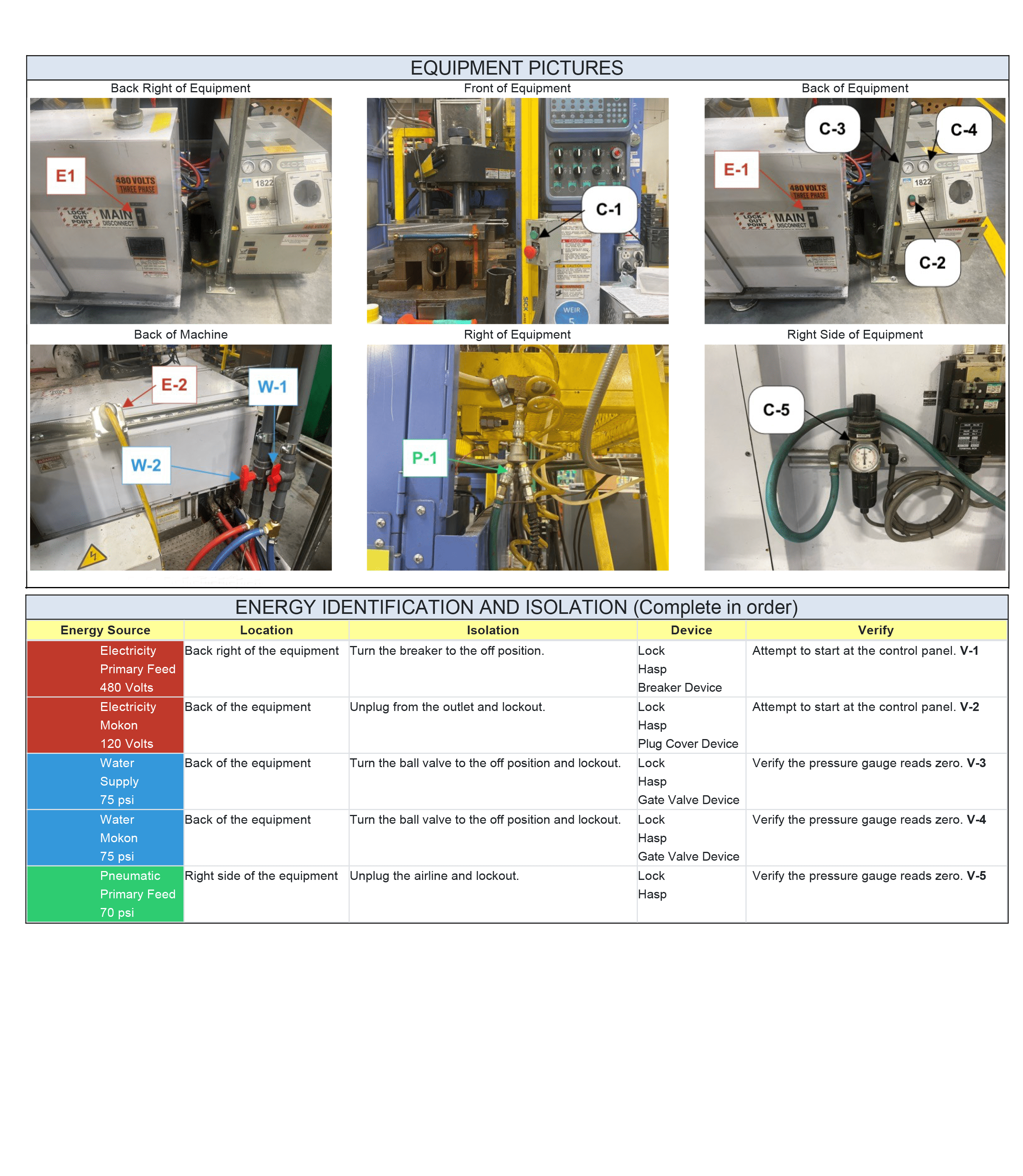
2. Incorporate A Variety Of Teaching Methods – Use different approaches to make your lockout tagout training more effective. Try methods such as verbal explanations, presentations, labeled equipment diagrams/photos, demonstrations, hands-on practice, video tutorials, case studies, role play or even short quizzes. Doing so will accommodate different learning styles and help your staff fully comprehend the training material.
3. Highlight Consequences and Accountability – Clearly state the potential consequences of non-compliance. (For a list, see the OSHA 1910.147 article). Workers need to understand the gravity of their actions and the impact that negligence can have – for their safety, the safety of others, and company well-being.
4. Invite Questions – Give trainees the opportunity to ask questions. Keep in mind, this might all be new information for some, which could seem overwhelming or difficult to remember. Questions allow you to provide clarity, minimize misunderstandings, and receive feedback.
5. Keep It Ongoing – Treat training as a continuous process of improvement rather than a singular event. Encourage workers to help one another and continue improving their craft. Continue to update your lockout tagout training with best practices and hold refresher courses as needed.
Documentation and Verification
To make your life easier and keep things up to date, make sure to keep records of all your lockout tagout training sessions. Document information such as:
- Names of training attendees
- Training date
- Trainer’s name
- Topics covered
- Questions
- Results from tests/practice
- Feedback/notes for improvement
Keeping these records will help you prove compliance, plan future training, and correct any unsafe practices.
Conclusion
Effective training is the foundation of a safe and compliant lockout tagout program. Training programs should cover the basics including the purpose of lockout tagout, its steps, LOTO roles, and equipment usage. It should also go into topics such as proper documentation, safety codes, and equipment-specific procedures. By providing employees with this key information, supervisors are able to significantly reduce the risk of accidents and maintain regulatory compliance. Building an effective training program isn’t easy, but it is definitely worth it. Well trained teams can rely on one another to get the job done correctly and safeguard one another from hazardous energy exposure.