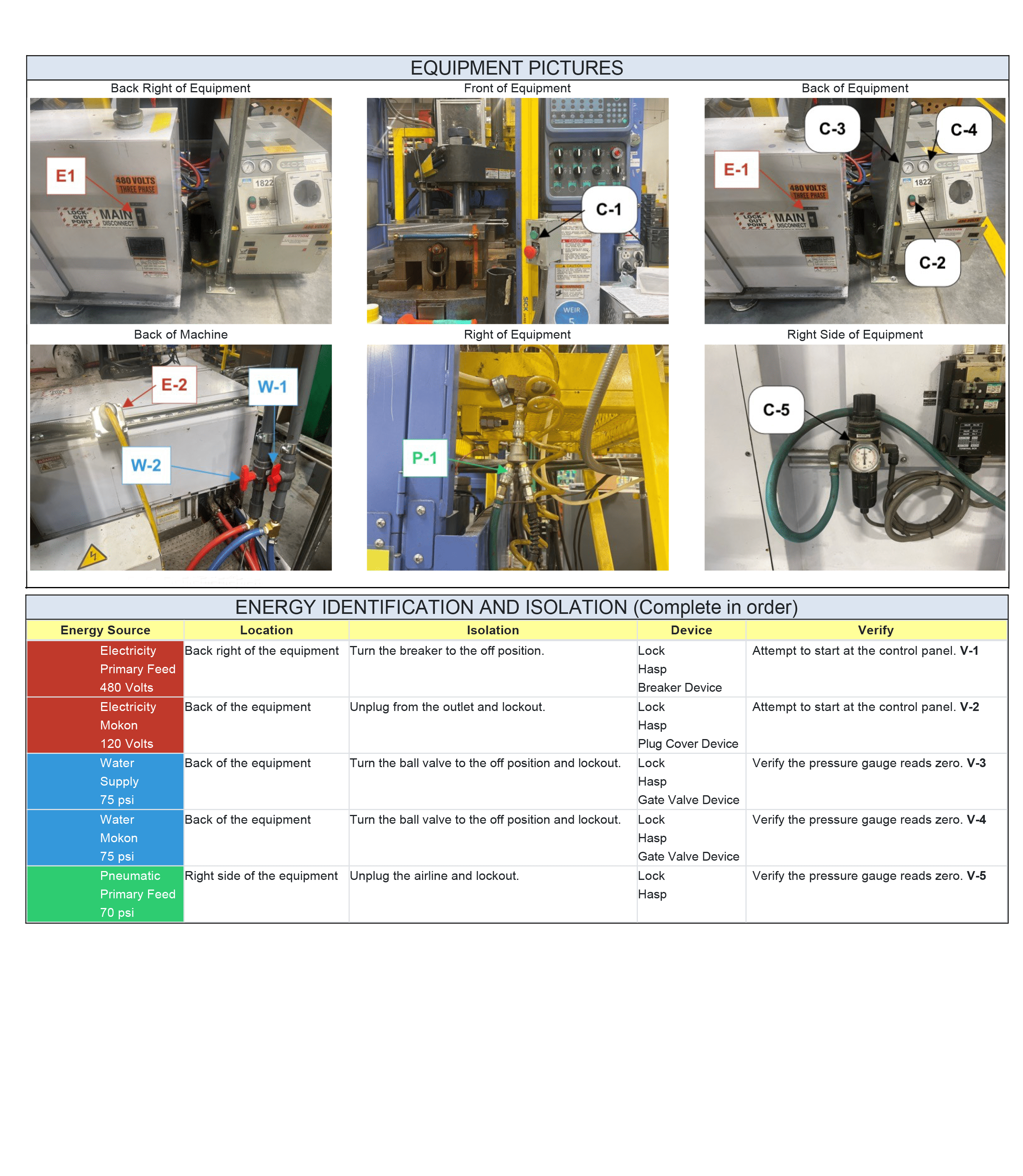
This article covers the main points for lockout/tagout codes, providing you with key information to stay compliant and master safety.
Did you know that non-compliance with lockout/tagout codes can lead to fines worth hundreds of thousands of dollars? Yes, you read that correctly. Hundreds of thousands of dollars. As a result, it is highly valuable for both experienced professionals and industry newcomers to know the applicable safety standards, remember their main points, and understand how to meet their requirements.
This article aims to provide readers with necessary information to master both lockout tagout safety AND compliance. In it we will break down the two primary codes referenced in the US. That way, you can feel confident and informed as you build a strong, legally compliant, and effective energy control program.
Which Safety Codes Should You Know for Lockout/Tagout?
In the US, there are two main safety codes that provide instruction and guidance for lockout tagout: OSHA 1910.147 The Control of Hazardous Energy (lockout/tagout) and ANSI Z244.1 Control of Hazardous Energy: Lockout, Tagout.
In the following sections, we will take a closer look at each of these safety codes.

OSHA 1910.147
Description: OSHA 1910.147 is a safety code established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. It is generally considered the primary federal regulation governing lockout tagout in workplaces. OSHA’s lockout/tagout code outlines the minimum requirements for protecting workers from hazardous energy sources during service or maintenance activities.
Main Points:
- Establishing an energy control program
- Written, equipment-specific LOTO procedures
- Training for authorized and affected employees
- Periodic inspections (at least annually)
- Use of lockout devices and/or tagout devices
Why it matters: Because OSHA is a government backed organization, they have the power to enforce compliance with their safety standards. Therefore, compliance with OSHA 1910.147 is mandatory. Lockout/tagout is one of the most commonly cited workplace safety violations and those who do not comply are subject to weighty fines, determined by the severity of the infraction.
For a more in-depth review of OSHA 1910.147, see our article here. It dives into all the specific requirements outlined in the code along with a breakdown of the various types of violations you can receive and their fine values.
ANSI Z244.1
Description: ANSI Z244.1 is a safety consensus standard created by the American National Standards Institute and the American Society of Safety Professionals. Similar to the OSHA standard, it outlines key information regarding the control of hazardous energy and the safe implementation of lockout/tagout. The key difference between the two is that OSHA’s is required by law and ANSI’s is more like a guide of best practices that individuals can voluntarily comply with.
Main Points:
- Encourages the creation of an energy control program, equipped with training materials and scheduled inspections.
- Offers recommendations for alternative protective measures (APMs)
- Covers complex systems, robotics, and advanced technologies
- Details group lockout, shift changes, and lockout coordination
- Promotes a risk-based approach to energy control
Why it matters: While it isn’t legally mandated like OSHA, ANSI Z244.1 is widely respected and used as a benchmark for industry standards. It is a great tool, especially for organizations looking to go beyond compliance and further improve safety.
Want a more detailed overview of the contents of ANSI Z244.1? Don’t worry. We’ve got you covered. Click the link here to access our deep dive into the ANSI Z244.1. It looks at the standards main points and highlights the key benefits of compliance.

Compliance With Lockout/Tagout Codes Matters
Compliance with lockout/tagout codes is essential because it
1). directly safeguards workers from serious injuries/death caused by the unexpected release of hazardous energy and
2). protects your business from the effects of non-compliance (i.e. costly fines, legal liabilities, operational disruptions, and reputational damage).
Adhering to lockout/tagout codes, including OSHA 1910.147 ad ANSI Z244.1, is about more than just obligation. It’s about demonstrating a commitment to workplace safety, risk management, organizational integrity, and a bright future for both your company and its employees.
Consequences of Non-Compliance with Lockout/Tagout Codes
As was previously mentioned, the government may issue fines to those who are found violating the established requirements in OSHA standards. Here are the types of violations that can be received and their current monetary value (as of Jan 2025).
- Other Than Serious Violation – capped at $16,550 per violation
- Serious Violation – capped at $16,550 per violation
- Willful Violation – capped at $165,514 per violation
- Failure to Abate – capped at $16,550 per day past the abatement date, up to 30 days
- Repeat Violation – capped at $165,514 per violation
To learn more about these violations and what qualifies you for a penalty, see this article describing OSHA 1910.147 and its associated penalties.

Software Simplifies LOTO Code Compliance
No matter what industry you are in, lockout tagout software can simplify your job.
Our LOTO software has been developed over the last 30 years and is specifically designed to help you write procedures, manage a LOTO program, and perform lockout tagout in a way that is easy, efficient, and compliant.
Want to learn more about what our LOTO software can do and how it can make your job easier? Schedule a demo to talk with one of our specialists.
Conclusion
In the world of lockout/tagout, there are two primary codes to know: OSHA 1910.147 and ANSI Z244.1. Each of these codes provides valuable information and requirements for performing lockout tagout. OSHA’s code is government-enforced while ANSI’s is complied with voluntarily. Though the content they provide is slightly varied, both codes should be strictly adhered to. Non-compliance can lead to many unfortunate outcomes including large fines, damaged property, or injured personnel. The best way to approach code compliance is with the help of lockout tagout software. It can take the guesswork out of compliance. Regardless, lockout/tagout codes provide a framework for conducting procedures safely and effectively. Those who take the time to learn and follow the guidelines in OSHA 1910.147 and ANSI Z244.1 will see the benefits in their improved understanding of safety and reduced risks.